Security considerations
OMniLeads is an application that combines Web (https), WebRTC (wss & sRTP), and VoIP (SIP & RTP) technologies. This implies a certain complexity when deploying it in production under an Internet exposure scenario.
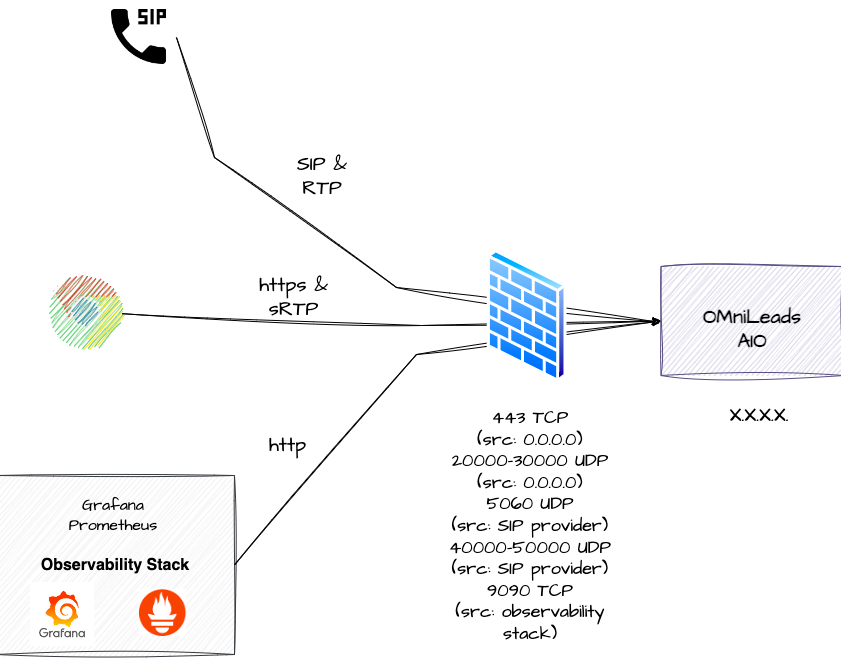
On the Web side of things, it is ideal to implement a Reverse Proxy or Load Balancer in front of OMniLeads, meaning exposed to the Internet (TCP 443) and forwarding requests to the Nginx of the OMniLeads stack. Regarding VoIP, when connected to the PSTN through VoIP, it is ideal to operate behind a Session Border Controller (SBC) exposed to the Internet. However, we can intelligently use Cloud Firewall technology when operating on VPS exposed to the Internet. Below are the firewall rules that will be applied to the All In One instance:
443/TCP Nginx: This is where Web/WebRTC requests are processed by Nginx. Port 443 can be opened to the entire Internet.
20000-30000/UDP: WebRTC sRTP RTPengine: This port range can be opened to the entire Internet.
5060/UDP Asterisk: This is where SIP requests for incoming calls from ITSP are processed. This port should be opened, restricting by source IP(s) of the PSTN SIP termination provider(s).
40000-50000/UDP VoIP RTP Asterisk: This port range should be opened, restricted to the source IPs of the PSTN SIP termination providers.
9090/TCP Prometheus (optional, only if you are monitoring with Grafana and Prometheus): This is where connections from the monitoring center, specifically from Prometheus Master, are processed. This port can be opened by restricting the source to the monitoring center's IP.
3100/TCP Loki (optional, only if you are centralizing container logs with Grafana and Loki): This is where connections from the monitoring center, specifically Grafana, are processed. This port can be opened by restricting it to the IP of the monitoring center.
Last updated